What Happens If Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) Are High in your Body?
High leukocytes can significantly affect your body, and understanding these effects is crucial for maintaining overall health. Leukocytes, also known as white blood cells, are an integral part of your immune system and play a vital role in defending your body against infections and diseases. However, when leukocyte levels become elevated, it can indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention.
Let us see the effects of high leukocytes and the potential implications for your well-being. We will also discuss the importance of diagnostic tests in identifying the root cause of high leukocyte levels and provide insights into potential treatment options.
What are Leukocytes?
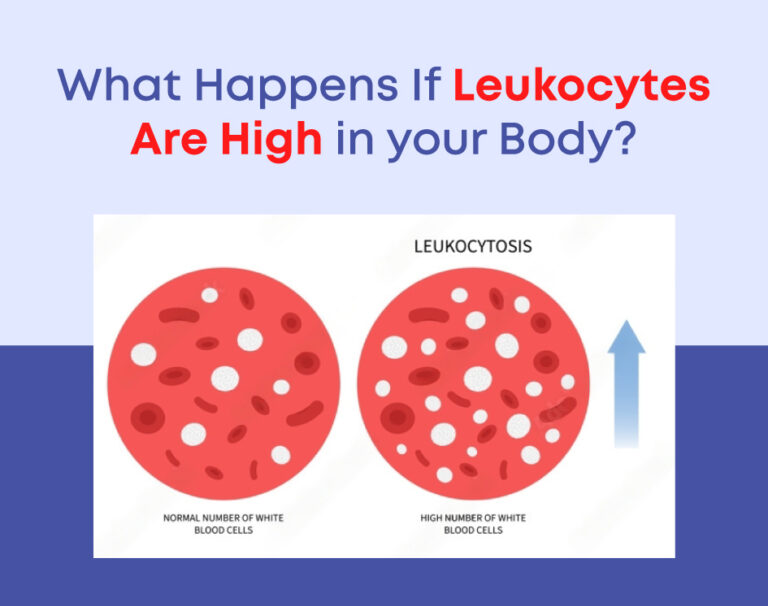
Leukocytes, commonly known as white blood cells, are a crucial component of your immune system. They play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases. An average leukocyte count in adults typically ranges from 4,500 to 11,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood. When the number of leukocytes exceeds this range, it is known as high leukocytes or leukocytosis. High leukocytes can be categorized into two types: relative and absolute leukocytosis.
Relative leukocytosis occurs when the proportion of white blood cells in the blood increases due to a decrease in the red blood cell count.
Absolute leukocytosis refers to an actual increase in white blood cells, regardless of the red blood cell count. Both types of leukocytosis can have different underlying causes and effects on the body.
White blood cells come in several types, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type has a specific role in the immune response. An increase in these white blood cell types can contribute to high leukocyte levels.
Causes of High Leukocytes
High leukocyte levels can result from various factors, including:
Infections: Both bacterial and viral infections can trigger an immune response, leading to an increase in white blood cells.
Inflammatory conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can cause high leukocytes due to ongoing inflammation.
Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus or multiple sclerosis can lead to high leukocytes as the immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues.
Medications: Certain drugs, such as corticosteroids or specific diuretics, can cause high leukocytes as a side effect.
Blood cancers: Types of cancers like leukemia or lymphoma can result in increased white blood cell production.
Symptoms and Signs of High Leukocytes
High leukocytes may not always cause noticeable symptoms, especially in mild cases. However, as levels increase, certain signs and symptoms may appear, such as:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Frequent infections
- Unexplained weight loss
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Symptoms related to the specific infection causing high leukocytes may also be present. For example,
Urinary tract infection: Pain or burning sensation during urination
Respiratory infection: Cough and difficulty breathing
These symptoms are not exclusive to high leukocytes and can be associated with other health conditions. Therefore, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests for High Leukocytes
When high leukocytes are suspected, diagnostic tests are necessary to identify the underlying cause. These tests can help determine the type of leukocytosis and the specific white blood cell count and provide insights into potential causes.
The most common diagnostic test for assessing leukocyte levels is a complete blood count (CBC). This test provides an overview of all the different types of blood cells.
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to determine the cause of high leukocytes. These tests can include:
- Blood cultures to identify bacterial infections.
- Imaging tests to detect abnormalities or tumors.
- Bone marrow biopsy to assess the production of blood cells.
Once the cause of high leukocytes is identified, appropriate treatment options can be explored.
Potential Complications of High Leukocytes
High leukocytes can lead to various complications depending on the underlying cause and severity. Acute leukocytosis, which occurs suddenly and resolves quickly, may have minimal complications. However, chronic leukocytosis persists over time and can have more significant implications. Here are some potential complications:
1. Increased risk of infections:
Excessively high white blood cell count may indicate an overactive immune response or an inability to combat infections effectively. This can lead to recurrent or severe infections that can have a detrimental impact on overall health.
2. Development of blood clots:
Increased leukocyte levels can contribute to the formation of blood clots. Blood clots can lead to severe conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, obstructing blood flow and causing damage to organs and tissues.
3. Risks associated with certain cancers:
Certain types of cancers, such as leukemia, can cause high leukocyte levels. Leukemia can affect the production of healthy blood cells and weaken the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections and other complications.
Treatment Options for High Leukocytes
The treatment for high leukocytes depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
- In cases where an infection causes high leukocytes, appropriate antimicrobial medications, such as antibiotics or antivirals, may be prescribed to address the infection and normalize white blood cell levels.
- Treatment for inflammatory conditions that contribute to high leukocytes may involve medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Immunosuppressant drugs may be prescribed for autoimmune disorders to suppress the immune response and reduce leukocyte production.
- In some instances, such as leukemia or lymphoma, cancer-specific treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy may be necessary to control cancer and normalize white blood cell counts.
Conclusion
High leukocytes can significantly affect the body, indicating an underlying health issue that requires attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications of high leukocytes is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Consult with your healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan if you have these signs and symptoms, or call us for experienced guidance.