Sepsis: Signs, Causes and Treatment For Blood Infection
Sepsis, also known as blood infection, is a life-threatening condition caused by the body’s overwhelming response to an infection. Despite its seriousness, many people are unaware of its existence, let alone its signs, causes, and proper treatment. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to recognize the early signs of sepsis, understand its causes, and be prepared to navigate the complex terrain of treatment options.
What Is Blood Infection And Why Is It Dangerous?
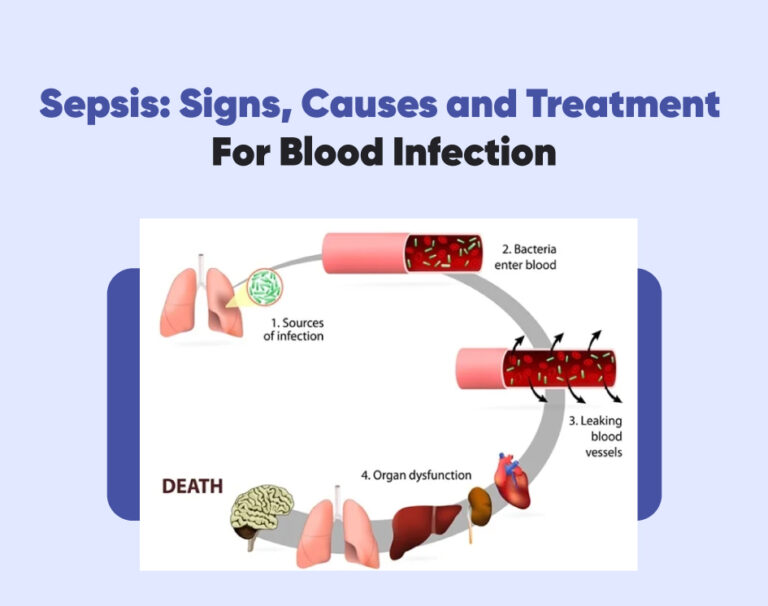
Sepsis occurs when the body’s response to an infection becomes dysregulated, leading to a systemic inflammatory response. This response can quickly escalate, affecting multiple organ systems and potentially leading to organ failure and death if not treated early. When infections from our body infiltrate and enter the bloodstream, it can lead to a systemic blood infection. What makes sepsis particularly dangerous is its ability to progress rapidly. Its symptoms can be vague and easily mistaken for other conditions. Also known as blood poisoning, sepsis can have severe consequences if not promptly recognized and treated.
Causes of Sepsis and How It Develops?
The most common cause of blood infection is a bacterial infection, although fungal or viral infections can also cause it. The condition can start in any part of the body, such as the lungs, urinary tract, or skin, and if left untreated, can spread throughout the bloodstream. Sepsis develops when the body’s immune system drops in response to the infection. Instead of targeting the invading pathogens, the immune response becomes hyperactive and begins to attack healthy tissues and organs. This excessive immune response leads to widespread inflammation and can result in organ damage and failure.
Risk Factors of Blood Infection
Sepsis can affect anyone, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this life-threatening condition. It’s essential to be aware of these risk factors to help identify individuals who may be more susceptible to sepsis. Here are some common risk factors:
- Age: Both infants and older people are at higher risk. Newborns and very young children have developing immune systems, while older individuals may have weakened immune function.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, cancer, and autoimmune disorders can weaken the immune system, making the body less able to fight off infections.
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Drugs used in organ transplantation and chemotherapy or to treat autoimmune diseases and cancer may suppress the immune response, resulting in a higher chance of getting blood infection.
- Respiratory or Kidney Failure: Conditions that compromise organ function can increase the risk of infections spreading and progressing to sepsis.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Sepsis
The signs of sepsis can vary depending on the individual and the stage of the infection. Still, there are some common indicators to look out for. The most prominent signs are:
- High fever, often accompanied by chills and shivering. This fever may not respond to usual fever-reducing medications and can persist despite treatment.
- Rapid heart rate and breathing. The heart may race, and the person may experience shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Additionally, a drop in blood pressure is often observed, leading to lightheadedness, dizziness, or even fainting.
- Other signs to watch for include a decrease in urine output, indicating kidney dysfunction, or a change in mental status, such as confusion, disorientation, or extreme sleepiness.
- The skin may appear mottled or discolored, and there may be signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge at the site of the initial infection. It is crucial to remember that sepsis can progress rapidly.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of sepsis is crucial for early detection and treatment of this potentially life-threatening condition.
Treatment for Sepsis
When it comes to sepsis, early and effective treatment is crucial to improve the chances of survival and prevent further complications. The treatment options for sepsis typically involve a combination of interventions to address the underlying infection, stabilize the patient, and support vital organ function. The first step in treating sepsis is
- Identifying the source of the infection through blood tests, imaging scans, or other diagnostic procedures. It allows healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate course of action.
- Antibiotics are usually administered immediately to combat the infection, and the choice of antibiotics depends on the suspected or identified pathogens.
- Intravenous fluids are administered to restore blood volume and maintain blood pressure, ensuring that vital organs receive adequate oxygen and nutrients. This process is carefully monitored to prevent complications such as fluid overload.
- In some cases, vasopressor medications may be required to raise blood pressure and increase blood flow to vital organs.
- Mechanical ventilation may also be necessary if abnormal respiratory function is noticed.
- Supportive care is integral to sepsis treatment as well. This may involve pain management, nutritional support, and close monitoring of vital signs and organ function.
- In severe cases, patients may require admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) for continuous monitoring and specialized interventions.
It’s important to note that sepsis treatment is a collaborative effort between the healthcare team and the patient. Navigating the treatment options for sepsis can be complex. Still, with timely intervention and comprehensive care, the recovery of sepsis can improve significantly. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect a blood infection, as early recognition and treatment are vital in combating this severe condition.
When Should You Talk To Your Healthcare Provider?
In conclusion, if you notice any of the critical signs associated with sepsis, such as unexplained fever or hypothermia, rapid heart rate, breathing difficulties, confusion, or low blood pressure, it is crucial to reach out to your healthcare provider without delay. Early recognition and medical intervention significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery in cases of blood infection. Don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider or call us if you suspect sepsis, ensuring that appropriate steps are taken to address this serious condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can bloodstream infection be treated?
Yes, bloodstream infections can be treated with appropriate antibiotics and supportive care.
How do you know if infection is in your bloodstream?
Signs of a bloodstream infection may include fever, chills, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and confusion. Laboratory tests, including blood cultures, can confirm the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream.
Can sepsis be cured?
Sepsis can be treated and managed with early detection, appropriate antibiotics, and supportive care. However, the outcome depends on the severity of the condition and the patients overall health.
Is blood infection very serious?
Yes, blood infections can be very serious, especially if not promptly treated. They can lead to severe complications such as sepsis, organ failure, and even death if left untreated.
What is the first stage of blood infection?
The first stage of a blood infection may involve the invasion of microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, or fungi) into the bloodstream, leading to an immune response and the onset of symptoms such as fever and chills.
Are blood infections contagious?
Blood infections are not typically contagious from person to person. They are usually caused by the entry of microorganisms into the bloodstream from another site of infection in the body.
Can blood infection cause cancer?
Blood infections themselves do not cause cancer. However, certain infections, such as chronic viral infections like hepatitis B or C, can increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer over time.
Is blood infection a serious problem?
Yes, blood infections can be a serious medical problem that requires prompt medical attention and treatment. If left untreated, they can lead to severe complications and even be life-threatening.
What is the most common cause of sepsis?
The most common cause of sepsis is a bacterial infection, often from lung, urinary tract, abdominal, or skin infections.