Pernicious Anemia: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, characterized by the body’s inability to absorb vitamin B12 efficiently. This condition can lead to a reduction in healthy red blood cells, causing various symptoms that affect overall well-being.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about pernicious anemia to help you or your loved ones take proactive steps toward better health.
What is Pernicious Anemia?
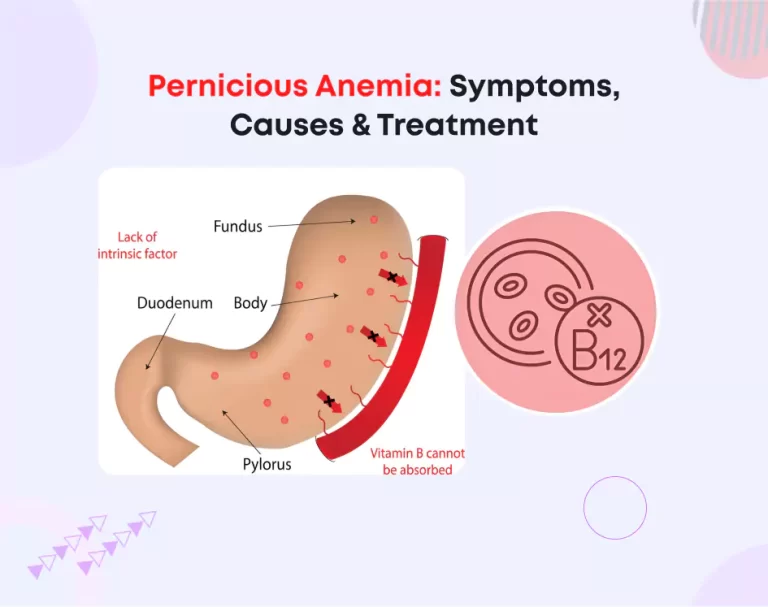
Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune disorder that prevents the absorption of vitamin B12 due to a lack of intrinsic factor—a protein produced by the stomach lining. Without sufficient vitamin B12, the body cannot produce enough healthy red blood cells, leading to a range of symptoms from fatigue to neurological complications. This condition is often categorized under megaloblastic anemia, where red blood cells become abnormally large and ineffective.
Key Symptoms of Pernicious Anemia
Recognizing the symptoms of pernicious anemia is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Extreme Fatigue: Persistent tiredness even after adequate rest.
- Pale or Jaundiced Skin: Due to reduced red blood cell production.
- Shortness of Breath: Often triggered by minimal exertion.
- Tingling Sensation: Numbness in hands and feet due to nerve damage.
- Cognitive Difficulties: Memory loss, confusion, and difficulty concentrating.
- Mouth and Tongue Issues: Red, swollen tongue and mouth ulcers.
- Heart Palpitations: Irregular or fast heartbeats.
If you experience these symptoms persistently, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing and diagnosis.
Common Causes of Pernicious Anemia
Understanding the root cause of pernicious anemia helps in managing the condition effectively. The primary causes include:
- Autoimmune Response: The immune system attacks stomach cells that produce intrinsic factors, preventing vitamin B12 absorption.
- Genetics: A family history of autoimmune disorders can increase the risk.
- Dietary Deficiency: Long-term lack of vitamin B12-rich foods like meat, dairy, and eggs.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease can interfere with B12 absorption.
- Surgical Factors: Gastric surgeries that affect intrinsic factor production can also lead to pernicious anemia.
Risk Factors Associated with Pernicious Anemia
Certain factors can elevate the risk of developing pernicious anemia:
- Age: More common in individuals over 60.
- Ethnicity: Higher prevalence among Northern European and Caucasian populations.
- Medications: Long-term use of antacids and metformin can impact B12 absorption.
Recognizing these risks can aid in preventive measures and early diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Pernicious Anemia
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing pernicious anemia effectively. Healthcare providers may use the following methods:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for enlarged red blood cells.
- Vitamin B12 Levels: Testing serum B12 levels to confirm deficiency.
- Intrinsic Factor Antibody Test: Detects antibodies preventing B12 absorption.
- Methylmalonic Acid Test: Elevated levels can indicate B12 deficiency.
Prompt diagnosis can prevent the progression of symptoms and complications.
Effective Treatment Options for Pernicious Anemia
Treating pernicious anemia focuses on replenishing vitamin B12 levels and managing symptoms:
- Vitamin B12 Injections: The most common and effective treatment, usually administered intramuscularly.
- Oral Supplements: High-dose B12 tablets may be prescribed if absorption is possible.
- Dietary Adjustments: Increasing intake of B12-rich foods like fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up blood tests to ensure adequate B12 levels.
Timely and consistent treatment can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent long-term complications.
Lifestyle Tips to Manage Pernicious Anemia
- Balanced Diet: Include B12-rich foods such as lean meat, fortified cereals, and dairy products.
- Avoid Alcohol: Excessive alcohol can impair nutrient absorption.
- Regular Exercise: Boosts energy levels and reduces fatigue.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor B12 levels.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes can significantly improve the quality of life for those managing pernicious anemia.
Complications of Left Untreated
Untreated pernicious anemia can lead to severe complications such as:
- Neurological Damage: Permanent nerve damage and cognitive impairments.
- Heart Issues: Increased risk of heart disease due to elevated homocysteine levels.
- Digestive Problems: Increased risk of stomach cancer and gastric polyps.
Timely treatment can help avoid these serious health risks.
Conclusion
Pernicious anemia is a manageable condition with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and following a prescribed treatment plan can significantly enhance the quality of life. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in managing this condition effectively. If you suspect you have symptoms of pernicious anemia, consult your healthcare provider promptly or consult with us to start your journey to better health.