Pediatric Hematology: Compassionate Care for Young Patients
In the world of medical fields, pediatric hematology stands out as a source of hope for kids with tricky blood problems. These brave children, dealing with different blood issues, get comfort and wise help from pediatric blood experts. This piece explores Pediatric Hematology, showing how important it is, the health troubles it deals with, and the vital part it plays in rescuing young folks.
Pediatric Hematology: What It Means and What It Does
The study of blood, called Hematology, deals with understanding how blood works and what goes wrong with it in sickness. It helps find and cure various blood issues. These issues can include things like not having enough blood (anemia), your body attacking itself (autoimmune diseases), or the scary blood cancer called leukemia. The tricky thing is that many blood problems can show up without any warning signs, so it’s super important to find them early and get them treated.
Pediatric Hematology brings this important part of medicine to children, ensuring that they get specialized care suited to their specific requirements. Each year, many children worldwide are diagnosed with cancer or leukemia, indicating an increasing trend that necessitates a caring response from the medical community.
The Pediatric Hematologist: A Lifesaving Specialist
A doctor who focuses on kids’ blood issues is called a pediatric hematologist. They work to find, treat, and stop blood problems in children. While the main ideas about blood sicknesses stay the same, how they appear can change a lot in kids, teenagers, and adults. That’s why pediatric hematologists are crucial. They make sure the treatment is just right for each young patient.
What diseases does a pediatric hematologist treat?
Pediatric hematologists confront a diverse range of blood-related issues in their daily practice in order to treat various conditions including:
Leukemia: Both acute and chronic forms of leukemia require expert management.
Anemia: Treating low red blood cell counts is critical for a child’s health.
Lymphomas: Pediatric hematologists play an important role in the treatment of lymphatic system cancers.
Myeloma: This malignant tumor of blood cells demands specialized care.
Hemophilia: Treating this bleeding disorder requires precision and expertise.
Cytopenia: Low blood cell counts necessitate close monitoring and intervention.
Bleeding Disorders: Managing conditions like Von Willebrand disease is essential.
Werlhof’s Disease: Also known as immune thrombocytopenia, it requires careful attention.
Neuroleukemia: This complex condition demands a comprehensive approach.
When Should You Consult a Pediatric Hematologist for Your Child?
Identifying when your child needs to see a pediatric hematologist is crucial. Certain symptoms should raise red flags and prompt you to seek specialized care:
- Drowsiness
- Chronic Fatigue
- Numbness of Fingers
- Excessive Sweating
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes
- Dizziness
- Decreased Appetite
- Pale Skin
- Unexplained Bruises or Bruising
- Prolonged Bleeding
- Nosebleeds
- General Malaise
- Dry Skin with Adequate Hydration
- Severe Itching
Additionally, if a close relative has a history of hematological diseases or if your child exhibits low hemoglobin levels, seeking consultation with a pediatric hematologist is prudent. In cases where birth weight was below average, and artificial feeding was necessary, early assessment is beneficial. Also, differing blood types or Rh factors between mother and child, or maternal anemia during pregnancy, warrant a visit to a hematologist in the early years of a child’s life.
Diagnosing and Treating Pediatric Blood Disorders
Pediatric hematologists employ a range of diagnostic and treatment methods to address blood diseases effectively. Diagnostic techniques include:
- General and Biochemical Blood Tests
- Ferritin and Transferrin Level Assessments
- Iron Level Measurement
- Tests for HIV and Hepatitis
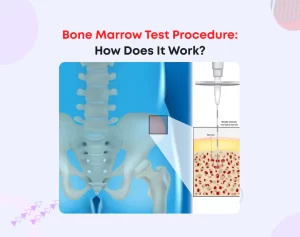
- Myelogram (Bone Marrow Smear Test)
Additional diagnostic modalities such as ultrasound, X-ray, and MRI may also be recommended to gain a comprehensive understanding of the condition.
Treatment strategies in the realm of pediatric hematology encompass:
- Complex Therapy
- Surgical Interventions
- Immunotherapy
- Hormonal Therapy
- Medications
- Chemotherapy
Each child’s treatment plan is carefully customized, forming a unique “protocol” designed to maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
The Significance of Early Diagnosis in Pediatric Hematology
In pediatric hematology/oncology, early and accurate diagnosis holds the key to effective treatment. Timely identification of the specific type of tumor is essential to initiate precise therapy. Increasing awareness among healthcare providers, especially general practitioners, is vital in recognizing potential oncological pathologies in children. This awareness ensures that young patients are referred to pediatric hematologists promptly, facilitating early diagnosis and treatment.
Modern diagnostic tools, including ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans, play pivotal roles in this process. They aid in identifying tumor characteristics and subgroups with different biological behaviors, paving the way for targeted and effective therapies. Organizations like ASEOP support pediatric oncohematology departments in their mission to provide cutting-edge care to young patients, investing in equipment, scholarships, and training programs.
The therapies are combinations, depending on the tumor type, of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiotherapy, to which the possibility of transplantation of bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells from peripheral blood and umbilical cord has been added in recent years. All these therapies are grouped into a specific therapeutic plan for each child called a “protocol.”
Surgery maintains a fundamental role in the therapy of pediatric tumors, even if today it is included in treatment protocols in which it is associated with chemotherapy and, depending on the case, radiotherapy. This allows the patient to undergo surgery when the volume of the tumor has already been reduced as a result of chemotherapy +/- radiotherapy, with greater possibilities of complete removal and less need for destructive interventions on vital organs and tissues. In bone sarcomas, for example, limb amputation operations are increasingly rare, and it is often possible to reconstruct the missing part and regain the functionality of the limb.
Nurturing Hope for Pediatric Hematology Patients
The cure rates of tumors in children in the advanced world vary according to the pathology, reaching 90% for some forms, while for others the rates are much lower. An intense research activity for these forms resistant to therapy is underway throughout the world, and blood cancer experts worldwide are fully participating in this activity.
In conclusion
Pediatric Hematology stands as a pillar of compassionate care for young patients facing blood-related challenges. The dedication of pediatric hematologists, coupled with advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment modalities, fosters hope and healing in the lives of countless children. As awareness grows and research flourishes, the future shines brighter for the next generation of pediatric hematology patients.