How Stem Cell Treatment Can Heal Your Bones ?
Your bones are not just hard and solid. They have a soft tissue inside them called bone marrow, which makes different kinds of blood cells. These blood cells are essential for your health and well-being. Sometimes, your bone marrow can get damaged or diseased by conditions such as cancer, infection, or genetic disorders. This can affect your blood cell production and quality, and cause serious problems for your body.
Stem cell treatment can heal your bones by replacing the faulty bone marrow cells with healthy ones. Stem cells are special cells that can turn into different types of cells, including blood cells. It can also help your bone marrow make normal blood cells again and improve your symptoms and outcomes. Stem cell treatment can be a lifesaving therapy for people with bone marrow diseases.
The Process of Stem Cell Treatment
Stem cell treatment for bone marrow diseases involves two main steps: harvesting and transplanting.
Harvesting
Harvesting is collecting stem cells from a donor or the patient. The stem cells can come from three sources: bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood.
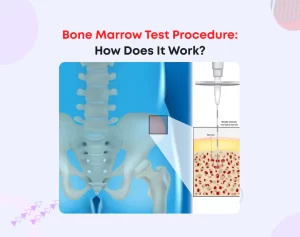
- Bone marrow: Bone marrow stem cells are obtained by inserting a needle into the hip bone or the breastbone and drawing out the marrow. This procedure is done under general or local anesthesia and may cause some pain and discomfort.
- Peripheral blood: Peripheral blood stem cells are obtained by giving the donor or the patient a medication that stimulates the stem cells to move from the bone marrow to the bloodstream. Then, the blood is drawn from a vein and passed through a machine that separates the stem cells from the other blood cells. The remaining blood cells are returned to the donor or the patient. This procedure is done without anesthesia and may cause some side effects, such as headache, nausea, or bone pain.
- Umbilical cord blood: Umbilical cord blood stem cells are obtained from the blood that remains in the placenta and the umbilical cord after a baby is born. This blood is collected and stored in a cord blood bank for future use. This procedure does not harm the mother or baby or cause pain or discomfort.
The harvested stem cells are then processed and stored until they are ready to be transplanted.
Transplanting
Transplanting is giving the stem cells to the patient through an intravenous (IV) line. The stem cells travel through the bloodstream and reach the bone marrow, producing new blood cells. This process can take several weeks or months, depending on the source and type of stem cells.
There are two types of stem cell transplants, they are autologous and allogeneic.
- Autologous: Autologous stem cell transplant uses the patient’s own stem cells. This type of transplant has a lower risk of rejection and infection. Still, it may not be effective for some bone marrow diseases, such as leukemia, affecting the stem cells.
- Allogeneic: Allogeneic stem cell transplant uses stem cells from a donor who is a close genetic match to the patient. This type of transplant has a higher risk of rejection and infection. Still, it may be more effective for some bone marrow diseases, such as leukemia, that require a new immune system to fight cancer cells.
Before the transplant, the patient may receive chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy the diseased bone marrow cells and make room for the new stem cells. This is called conditioning, and it may cause side effects, such as hair loss, nausea, vomiting, mouth sores, or fatigue.
Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment:
- Enhanced Blood Cell Counts: Stem cell therapy improves the quality and quantity of blood cells, enhancing overall health and vitality.
- Effective Symptom Alleviation: It successfully reduces complications and symptoms related to bone marrow diseases, providing relief and improved well-being.
- Increased Survival Rates: Stem cell treatment contributes to higher survival rates, extending life expectancy for individuals facing bone marrow challenges.
- Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells have the potential to regenerate damaged tissues, promoting healing and restoring functionality.
- Personalized Treatment Approach: Tailored stem cell therapies can address individual patient needs, offering a personalized approach to healing.
- Reduced Relapse Risk: Stem cell treatment lowers the risk of disease relapse, providing a more sustained and long-term solution for patients.
Who Is Eligible for Stem Cell Treatment:
- Bone Marrow Disease Diagnosis: Individuals diagnosed with bone marrow diseases, such as leukemia, lymphoma, or genetic disorders impacting blood cell production.
- Failed Conventional Treatments: Patients who have not responded well to traditional treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Medically Fit Candidates: Those deemed medically fit for the transplant process, taking into consideration overall health and potential treatment side effects.
- Willingness to Undergo Conditioning: Patients willing to undergo pre-transplant conditioning, which may involve chemotherapy or radiation to prepare the body for new stem cells.
Take away
Stem cell treatment for bone marrow diseases holds immense potential in healing bones by replacing damaged marrow cells with healthy ones. Despite its transformative benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks like infection, rejection, relapse, or infertility. If considering this option, consulting with a haematologist is advisable, ensuring a thorough evaluation of the pros and cons before making a decision. Remember, informed decisions pave the way for transformative healing.