Blood Clot Prevention: Early Warning Signs & Treatment
Do you suffer from throbbing pain and redness in certain body parts? It might be possible that you have developed a blood clot. Blood clots can have severe consequences on your body if left untreated. Keep reading to discover the causes, early warning signs, and available treatments for maintaining blood health.
What Are Blood Clots And How Do They Form?
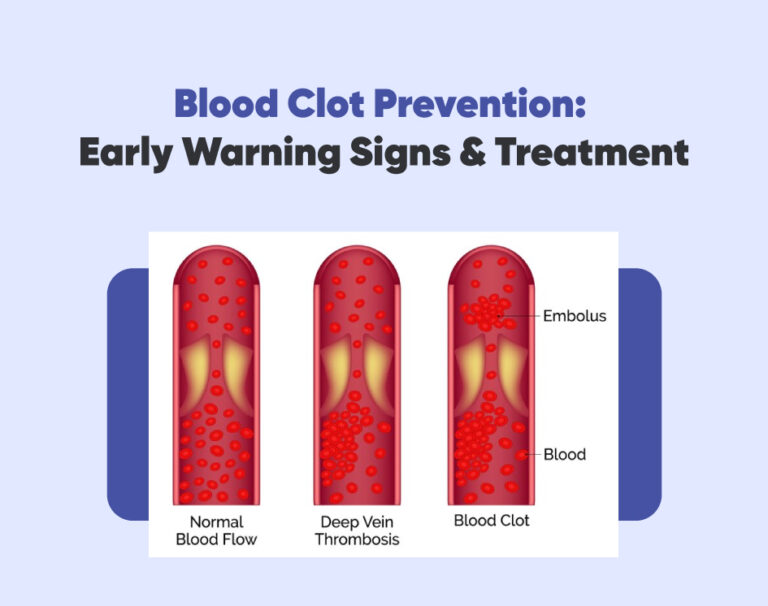
Blood clots, medically known as thrombosis, occur when blood thickens and forms a gel-like mass. They can develop in both the veins and arteries of the body. Thrombosis occurs when blood clots form within blood vessels, potentially leading to serious health complications. Thrombophilia, an inherent blood clotting disorder, induces abnormal blood clotting and amplifies the risk further. Blood clotting is a necessary process that helps prevent excessive bleeding when we get injured. However, problems arise when blood clots form unnecessarily or don’t dissolve properly, leading to potential health complications.
The formation of blood clots typically begins when there is damage to a blood vessel. This triggers a series of complex reactions within the body. Platelets, tiny cell fragments responsible for clotting, rush to the injury site and begin sticking together to form a plug. This initial clot is known as a platelet plug. To enhance the sealing of the plug, the body generates a net-like material known as fibrin. Fibrin acts as a net, trapping more platelets and blood cells, eventually forming a blood clot. While blood clots are essential for wound healing, they can become dangerous when they form inside blood vessels without an apparent reason. These abnormal blood clots can block blood flow, leading to severe complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Early Warning Signs of Blood Clots
Blood clots can occur in various body parts, such as the legs, lungs, or brain. By being aware of the early warning signs, you can take proactive steps to prevent the formation of blood clots and seek medical attention if necessary.
One of the most common early warning signs of blood clots is swelling and pain in the affected area. For example, if you notice
- sudden swelling,
- redness, or
- warmth in your leg.
It could be a sign of a blood clot in your deep veins, known as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
Similarly, if you experience
- chest pain,
- difficulty breathing, or
- sudden shortness of breath.
It may indicate a blood clot previously formed inside your body traveled through veins and reached your lungs. This condition is known as Pulmonary Embolism.
Other symptoms that may indicate the presence of a blood clot include unexplained pain or tenderness, especially in your arms or legs, and a heavy or achy feeling in the affected area. You may also notice changes in skin color, such as redness or discolouration, and the site may feel unusually warm to the touch. Pay attention to any unusual changes in your body and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
Common Risk Factors For Developing Blood Clots
While blood clots can occur in anyone, certain factors increase the likelihood of their formation, such as
- Prolonged Immobility slows down blood flow, increasing clot formation.
- Obesity strains veins, hindering proper blood flow.
- Smoking releases chemicals that damage blood vessels.
- Medical Conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders.
Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clots
It’s important to note that the symptoms of blood clots can vary depending on their location in the body. Some people may not experience noticeable symptoms, making it even more important to recognise signs proactively.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have a blood clot, seeking medical attention is crucial.
1. Swelling: Notice any unexplained swelling, particularly in the legs or arms. If one limb appears larger than the other or there is sudden swelling without an injury, it may be a cause for concern.
2. Pain or tenderness: Look out for localized pain or tenderness, especially in the affected area. It may feel like cramping or a persistent ache that doesn’t go away.
3. Redness and warmth: Keep an eye out for areas of redness or heat on your skin, particularly around the clot site. This can be an indication of inflammation and restricted blood flow.
4. Skin discolouration: Check for any unusual skin discolouration, which may appear bluish or pale in the affected area. This can be a result of compromised circulation.
5. Shortness of breath: If you experience sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or rapid breathing, it could be a sign that a blood clot has traveled to your lungs. Seek medical attention immediately if you encounter these symptoms.
Remember that these signs are not definitive proof of a blood clot, but they should alert you to the possibility of further investigation.
Treatment Options for Blood Clots
When thrombosis or DVT occurs, appropriate treatment is crucial. One common treatment option is using anticoagulant medications, also known as blood thinners. These medications help to prevent new clots from forming and existing clots from getting more significant. Individuals with thrombophilia may require long-term anticoagulation therapy. In severe cases, medical procedures such as thrombectomy or inserting a vena cava filter may be considered.
In some cases, more aggressive treatment measures may be necessary. Thrombolytic or clot-busting therapy involves using medications that can dissolve blood clots. This treatment is typically reserved for more severe cases and is administered intravenously. When a clot is causing severe symptoms or is located in a critical area of the body, a surgical option such as thrombectomy is suggested, where the lump is physically removed, or a catheter is placed to deliver medications directly to the clot. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine each case’s most appropriate treatment plan.
Seek Prior Medical Attention
When it comes to preventing blood clots, staying vigilant is crucial. While there are immediate actions you can take to reduce the risk, it is equally important to adopt long-term strategies to stay ahead of the game.
First and foremost, maintaining an active lifestyle is essential. Regular exercise improves overall cardiovascular health and promotes healthy blood circulation, reducing the chances of blood clots forming.
Conclusion
Additionally, it is crucial to stay hydrated. Drinking an adequate amount of water. Furthermore, if you have a sedentary lifestyle due to work or other factors, take regular breaks to move around and stretch your legs. Lastly, if you are at a higher risk of blood clots due to certain medical conditions or family history, consult your healthcare professional about preventive measures such as medications.






