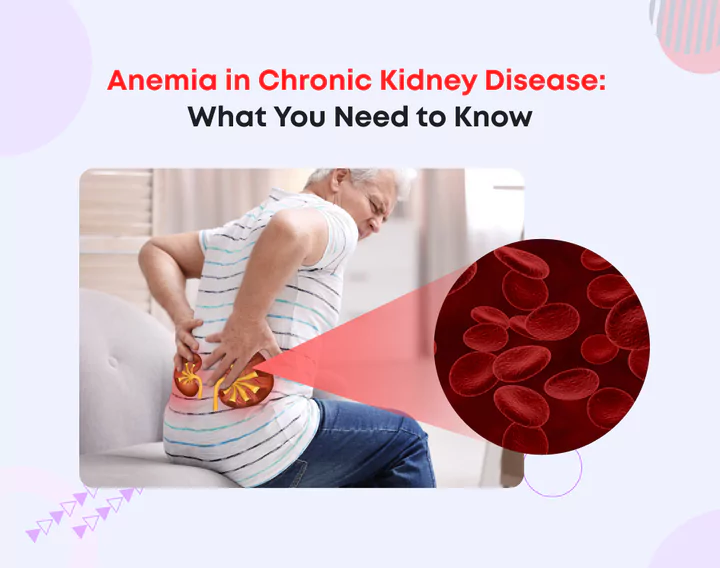
Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: What You Need to Know
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) impacts millions of individuals worldwide. It can lead to numerous complications, one of the most common being anemia. Anemia occurs when the blood has a lower-than-normal number of red blood cells, vital for carrying oxygen throughout the body. For those with CKD, anemia can significantly impact the quality of life, causing fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms that complicate their condition.
Understanding anemia in the context of chronic kidney disease is crucial for managing it and improving overall health. This blog will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for anemia in chronic kidney disease.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Chronic kidney disease is a persistent condition characterized by impaired kidney function. This section outlines the basics of this issue.
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease can arise from multiple factors that gradually harm the kidneys.
Diabetes: Increased sugar levels in the blood lead to damaged blood vessels in the kidneys.
High Blood Pressure: Increased pressure can harm kidney tissues.
Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units.
Polycystic Kidney Disease: A genetic disorder that leads to cysts forming in the kidneys.
Prolonged Obstruction: Blockages from stones or an enlarged prostate can cause damage.
Recurrent Kidney Infections: Ongoing infections can lead to chronic damage.
Knowing the cause of CKD helps in managing the disease effectively.
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease often progresses silently, showing symptoms only when the damage is advanced:
Fatigue: Due to poor filtering of waste and toxins.
Swelling: In the feet, ankles, or hands due to fluid buildup.
Urination Changes: Frequency and colour changes in the urine.
Nausea: Caused by toxin buildup in the blood.
Muscle Cramps: Resulting from electrolyte imbalances.
Itchy Skin: Due to waste accumulation in the bloodstream.
Early detection and treatment can effectively manage these symptoms.
Understanding Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Anemia, is often seen in patients with chronic kidney disease. This section will explain why CKD leads to anaemia and its effects.
Causes of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Several factors contribute to anemia in chronic kidney disease patients:
Reduced Erythropoietin Production: Kidneys produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. Kidneys that are damaged produce reduced amounts of this hormone.
Iron Deficiency: CKD can impair iron absorption or increase iron loss.
Blood Loss: Dialysis or frequent blood tests may result in blood loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor diet can contribute to a lack of essential nutrients.
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in CKD can suppress red blood cell production.
Understanding these causes helps in addressing anemia effectively.
Symptoms of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Anemia can significantly impact the daily lives of chronic kidney disease patients. Common symptoms include:
Fatigue: A constant feeling of tiredness.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing due to low oxygen levels.
Pale Skin: Reduced red blood cells cause paleness.
Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or faint.
Cold Hands and Feet: Poor circulation can cause a cold sensation.
Rapid Heartbeat: Increased heart beats due to intense pumping of oxygen.
Recognizing these symptoms can lead to timely treatment and a better quality of life.
Diagnosing Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Accurate diagnosis is key to managing anemia in chronic kidney disease patients. Here’s how anemia is typically diagnosed.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for diagnosing anaemia in CKD:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures overall red blood cells, haemoglobin, and hematocrit levels.
Serum Ferritin: Test used to check iron storage in the body.
Transferrin Saturation (TSAT): Measures how much iron is bound to the protein transferrin.
Serum Erythropoietin: Measures erythropoietin levels to assess kidney function.
Regular blood tests help monitor anemia and guide treatment.
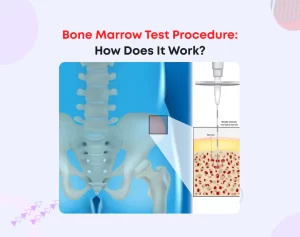
Bone Marrow Examination
In rare cases, a bone marrow exam may be needed:
Bone Marrow Biopsy: Examines marrow for abnormalities in red blood cell production.
This test is usually for complex cases where the cause of anemia is unclear.
Treatment for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Treating anemia in chronic kidney disease involves addressing its root causes and managing symptoms. Here’s a look at various treatment options:
Iron Supplements
Iron is crucial for making red blood cells. Iron Supplements can help:
Oral Iron: Easy to take but may cause stomach upset.
Intravenous Iron: Used if oral iron supplements are ineffective or not well tolerated.
Iron supplements should be taken under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
Erythropoiesis-stimulating Agents (ESAs)
ESAs stimulate red blood cell production:
Synthetic Erythropoietin: Injections given to boost red blood cell counts.
Dosage and Monitoring: Dosages are tailored to individual needs, with regular monitoring.
ESAs can significantly improve symptoms of anemia in CKD patients.
Blood Transfusions
In severe cases of anemia in chronic kidney disease, blood transfusions may be necessary:
Immediate Effect: Provides quick relief from severe anemia symptoms.
Risks: Possible risks include infections or immune reactions.
Transfusions are typically reserved for emergencies or when other treatments fail.
Dietary Adjustments
A healthy diet supports anemia management:
Iron-rich foods: Include meats, beans, and leafy greens.
Vitamin B12 and Folate: Necessary for red blood cell production.
Limit Phosphorus: Too much phosphorus can worsen kidney disease.
Consulting a dietitian can help CKD patients plan a balanced diet.
Managing Underlying Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
Addressing the underlying causes of anemia can improve outcomes:
Control Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can worsen kidney function.
Manage Diabetes: Keeping blood sugar levels stable helps protect the kidneys.
Treat Infections: Prompt treatment of infections can prevent further damage.
Managing underlying health issues is crucial for controlling anemia.
Living with Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Living with anemia and chronic kidney disease requires a comprehensive approach. Here’s how patients can improve their quality of life.
Regular Monitoring
Regular health check-ups are essential:
Routine Blood Tests: Monitor red blood cell levels and iron stores.
Doctor Visits: Regular consultations to adjust treatment plans.
Consistent monitoring helps in early detection and management of complications.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple lifestyle changes can result in better outcomes:
Stay Active: Light exercise can boost energy levels.
Adequate Rest: Ensure enough rest to combat fatigue.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps kidney function.
Lifestyle adjustments can enhance overall well-being.
Emotional Support
Emotional well-being is equally important:
Join Support Groups: Connecting with others can provide emotional support.
Counselling: Professional counselling can help manage stress and anxiety.
Having a strong support system is valuable for effectively managing chronic conditions.
Wrapping Up
Anemia is a significant concern for those with chronic kidney disease, impacting their health and daily life. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing the condition effectively. Regular monitoring, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments can improve outcomes for chronic kidney disease patients suffering from anemia. By staying informed and proactive, patients can lead a better quality of life despite their condition. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to individual needs.